Practical 2
ISOLATION OF MICROALGAE
Introduction
Microalgae culture is so important have lot
of benefit. But it is hard to have a pure culture of algae because there will
be a lot of species in one culture. To have a single species culture, isolation
of microalgae is needed. There is a few techniques to isolate a microalgae such
as,
a)
Single cell isolation by using
micropipette
b)
Streaking samples on agar
plates
c)
Isolation by dilution
Material
and methods
Single
cell isolation by using micropipette
Materials: Culture Water, Bunsen burner,
lighter, microscopic glass slide, Pasteur pipette, forceps, compound microscope
1)
Pasture pipette is placed over
the flame of the Bunsen burner.
2)
Using forceps, the tip of Pasteur
pipette became soften and being pulled to make it longer and small hole.
3)
The ends of the pipette should be
smooth to prevent it from destroying algae cell.
4)
The pipette was then connected
to a rubber hose/tubing.
5)
A drop of sample was dropped on
glass slide and was placed under the compound microscope, the micropipette was
used to pick up cells different cells and then dropped on to the side of the
glass slide.
6)
Finally, the single cell is
transferred to the media in one of the well in a 96-well plate.
Streaking samples on agar plates
Materials: f/2 agar plates, f/2+si agar
plates, inoculation loop, Bunsen burner, centrifuge, Epperndorf tubes.
Methods:
1)
1 mL of sample was insert into
an Epperndorf tube and being centrifuged at 5000rpm for 10minutes.
2)
Inoculation loop were sterile
by putting the loop tip on the flame of Bunsen burner and let it cool down for
15 sec.
3)
The cell pellets at the bottom
of Epperndorf tube were picked up with a inoculation loop and was streaked on
the agar which is two type of agar, f/2 and f/2 + si.
4)
The plates were then incubated
under room temperature with the presence of fluorescence light.
5)
Observation on the streaking
plate being done after two weeks.
Figure 3 : Streaking sample on agar technique
Isolation
by dilution
Materials: 10 test tubes, seawater, micropipette,
stock culture
Methods:
1)
10 test tube being filled up with
9ml of water.
2)
Then 1ml of stock culture being
inserted into test tube 1 and being mixed using micropipette.
3)
1ml of mixed culture in test
tube 1 being transferred into test tube 2 and being repeated until test tube
10.
4)
The test tubes were then kept
under room temperature and under the presence of light.
5)
The growth of algae was
observed daily. It is indicated by the changing color of the media.
Result
a) Single cell isolation by
using micropipette
None species was successfully being
isolated using this method.
b) Streaking samples on agar
plates
c) Isolation by dilution
This method was not successful because
there is no bacteria growth.
Discussions
All method to isolate microalgae has their
difficulty and successful rate. For single cell isolation using micropipette,
high skill is needed to isolate one species of microalgae from one drop of
water. Lot of time needed to search one cell of microalgae and will be
difficult to isolate moving microalgae.
For streak plate method, this method is
easy and can be practiced by everyone. But the result for streak plate method
cannot be expected because of the sample that was taken might have several
species or the agar plate being contaminated by other bacteria.
For dilution method, stock culture is
needed because serial dilution is needed in this method. Dilution will be done
for 10 times using 10 test tubes. Dilution is needed to decreased the number of
microalgae cell in culture stock.





 Figure 6 : F/2
Figure 6 : F/2 Figure 7 : F/2 + Silica
Figure 7 : F/2 + Silica Figure 8 : F/2 + Silica
Figure 8 : F/2 + Silica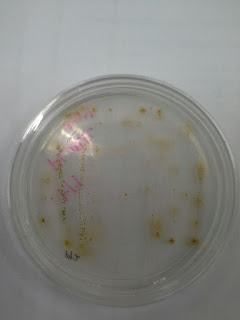 Figure 9 : F/2
Figure 9 : F/2 
No comments:
Post a Comment